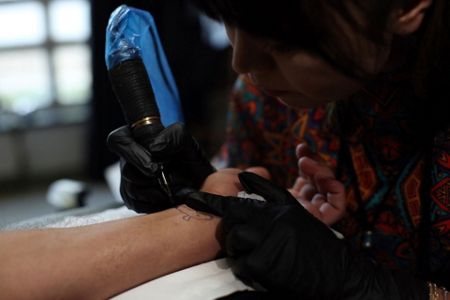
KABUL, Afghanistan (AP) — A female tattoo artist, a rarity in ultra-conservative Afghanistan, is taking a big risk with every customer she takes on.
It’s been 18 months since Suraya Shaheedi started her mobile tattoo shop in the capital, Kabul. She’s received death threats for taking on the taboo of the ink-on-skin drawings she does — as well as being a single woman willing to work with men.
“I have struggled a lot, even been threatened with death, because people in Afghanistan think doing tattoos is haram,” she said, using the Arabic word meaning prohibited by religion.
“Whether my customers are men or women doesn’t matter to me. I do tattoos for both,” says Shaheedi, a 26-year-old, divorced single mother.
In a black curtained room, surrounded by his friends, a young customer shrieks in pain as the needle pierces and inks his skin.
“I can’t leave the profession I love,” Shaheedi adds.
She easily gets customers, whether men or women, as social attitudes toward tattoos loosen up and more ink parlors open. It’s the kind of small, but important change that Shaheedi feels a return of Taliban rule could threaten.
After decades of war, Afghans want peace. A big concern for many like Shaheedi is that U.S.-led peace talks with the Taliban will boost the militant group.
“I am happy if the Taliban return results in peace, but if they disagree with my work and impede the freedom and progress of women, then I will be the first to stand against them,” she vowed.
Women like Shaheedi have carved out a space for themselves in a society where custom heavily restricts women’s roles and education. Close to 40% of Afghanistan’s eligible girls are not allowed by their families to go to school, and almost 20% are forced by their families to leave school after grade six, according to a survey by the Asia Foundation released this year.
In areas under the Taliban, who now control or hold sway over roughly half of the country, women are not allowed to leave their homes without a male escort. The insurgent group ruled Afghanistan with a harsh version of Islamic law from 1996 to 2001, when the U.S. invaded.
Shaheedi divorced her husband eight years ago while she was pregnant. She and her son now live with her parents. Her father supports her work, even though Afghanistan’s patriarchal society often forbids a woman from touching a man to whom she is not related or married.
Her parents and elder brother persuaded her to become a tattoo artist, Shaheedi said, after she got her first tattoo while visiting Turkey — an arrow piercing the image of an eye on her right hand, which she says symbolizes overcoming adversity.
Shaheedi’s father, Hussain, 58, believes the strict customs controlling women in Afghanistan need to change. “I support my daughter in every way, and she makes me proud the way she’s stood against this taboo,” he said.
Shaheedi uses Instagram and other social media to find and meet customers. She prefers not to keep a parlor with a fixed address out of concerns for her safety.
She also does manicures and makeup. When she met one customer recently at a hair salon, the customer’s husband recognized her from her social media pages as being the tattoo artist “Ahoo,” the nickname she uses online. The husband threatened to kill Shaheedi if she kept posting images of her tattoo work on social media.
Tattoos were common in some of Afghanistan’s rural areas, especially among Pashtun and Hazara women, but the ink piercings were used sparingly, often as only a few green dots on the face.
Tattoo artists say demand among the younger generation has risen for more flamboyant and personal designs, and with it, the number of ink parlors increased in the capital.
Omid Noori, 23, has 16 tattoos all over his body. He wants to add another on his left arm, showing the head of a lion with a crown and wreaths. But he only wants new designs on parts of his body that his clothing can hide, because he says he’s tired of hearing people’s negative comments about the ink piercings.
He also worries what would happen if Islamic militants caught him.
“I’m thinking that if the Taliban return, they’ll cut off my hands and legs,” he said.
He inked his last tattoos at a parlor belonging to a former Afghan army officer, Nazeer Mosawi.
Mosawi, 42, fought for seven years in Afghanistan’s civil war with the Islamic insurgents. He says he is still fighting the war, but this time his battle is against society’s conservatism, with his tattoo machine as his weapon.
Mosawi receives threatening phone and social media messages almost every day, demanding he close his tattoo business. “They even threaten to beat me, burn my shop,” he said. “There is no alternative: I tell them, OK, I can’t flee this country because of these threats. It’s my homeland.”
But for every threat he gets, Mousawi said he gets several messages with positive feedback or people curious to learn more.
Shaheedi said she is also working to put her 8-year-old son, now in second grade, through school. She is also studying business management at a university in Kabul.
“Being a woman in Afghanistan requires guts,” she said. “I am proud of myself for having the guts.”
Copyright 2019 The Associated Press. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed.